The "last mile" of medicines
You would like to know more?
Contact us
The term “last mile” is shrouded in a touch of magic. It is the final step to a destination, for example from the telecommunications line to one’s own home. But what about pharmacies, pharmaceutical wholesalers and patients? The “last mile” also has an impact on them. Global trends will change the challenges of the last mile in the future, that is certain. What could solution strategies look like?
Global Trends
Already today, the “last mile” accounts for about 40% of logistics costs for pharmaceutical wholesalers. Urbanization and the growth of e-commerce will continue to drive up costs. It is expected that the fleet of delivery vehicles will grow by up to 36 % by the end of 2020. The consequences: more CO2 emissions and more congestion in city centers.
Does more e-commerce also mean more traffic?
The healthcare market is changing – both digital searches and orders are increasing significantly. This means that direct deliveries and pharmacy deliveries are on the rise. Traffic on the “last mile” will increase by about 69 % in the next few years due to e-commerce orders. This contrasts with a reduction in private transport of approx. 32 %, because consumers are increasingly making fewer purchases in city centers.

Interventions and their effects
In order to counteract the trends, market participants need to look at innovations and interventions from six categories:
- Use of alternative vehicles
- Secured delivery
- Takeover of the “last mile” by customers
- Consolidation of supply
- Alternative delivery options
- Changed framework conditions for companies and in the public sector
If the scenarios are applied to the pharmaceutical industry, wholesalers and local pharmacies, they have a significant impact on emissions, delivery costs, congestion and competitiveness. For example, the use of electric vehicles can reduce last mile CO2 emissions by up to 60% – locker systems have the potential to reduce costs by around 12% and congestion rates by around 18%. Night delivery even reduces costs by up to 28 % and reduces congestion by a maximum of 21 %.
Business model and timeline
Depending on the strategy, the new business model can be characterized by 4 different categories:
- City Archetype: which city type do I focus on delivering my goods to?
- Delivery Types: what freight do I deliver?
- Adaptation Scenario: how regulated is my destination?
- Output Factors: what factors (profit, environment, image) do I value?
A successful and future-proof model can certainly only be developed from a combination of several factors. But the fact is: it is time to think about tomorrow in order to be able to react successfully to future changes.
You might also be interested in
Sustainable supply chain between wholesalers and pharmacies
FMD in Pharmaceutical Wholesale
What requirements will the FMD regulations introduce for wholesale in particular? Guido Lübeck reported on how GEHE is dealing with the topic.
Securpharm – Players in the Security Network
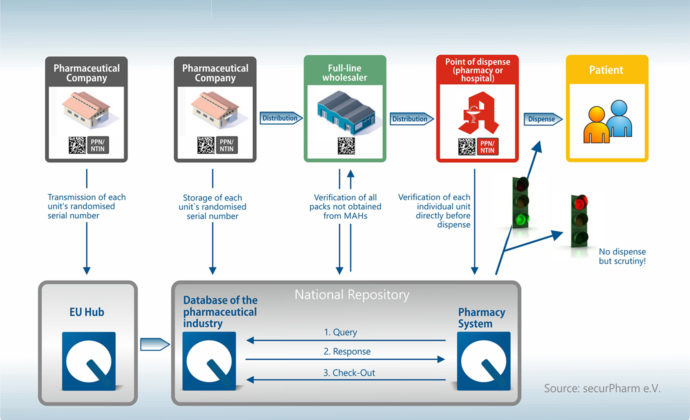
Each player makes an important contribution to the check. It all begins with the pharmaceutical manufacturer and ends with the handover of the medicine to the patient – usually in public pharmacies.